In the situation when network device is not supporting NetFlow protocol, the concept of Traffic Patterns allows you to redirect traffic to the server with a netflow probe. The netflow probe analyzes traffic and generates netflow traffic. We will call the server on which this probe is started the NetFlow Daemon Server. Figure below shows an example of this situation:
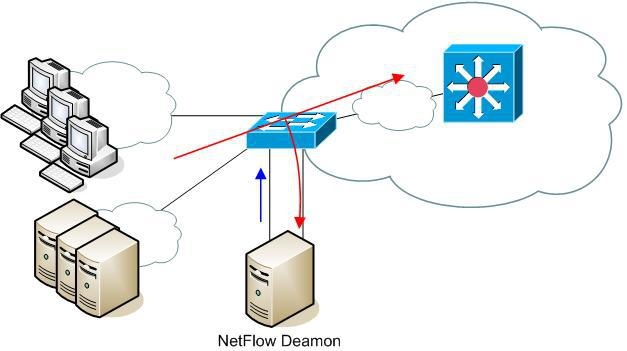
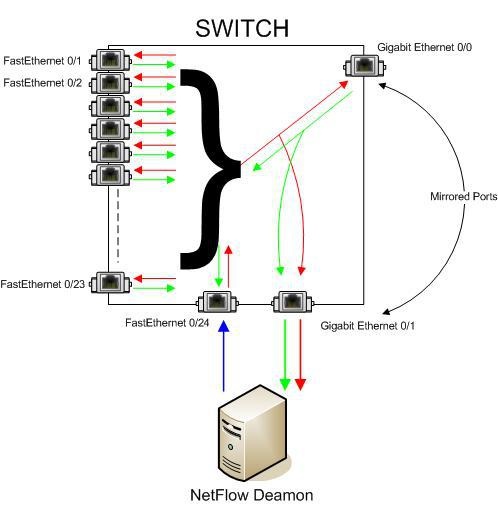
Figures above show the redirection of traffic (port mirroring) to the server on which the NetFlow Daemon Server is started. When the port mirroring is started on a switch, interface to whom all traffic is directed to becomes useless for normal device communication. It only passes all of its traffic (In and Out) from port mirroring interface.
The problem is: How to export netflow traffic if the interface on which the NetFlow Daemon Server is connected to is unusable for normal communication?
One solution is to add additional network card to the server and connect to the switch. This configuration enables netflow exporting even from the L2 switches. The drawback is the additional port utilization on the switch and the need for an additional server. One port on the switch is used for receiving mirrored In/Out traffic and another one for exporting netflow traffic. The blue arrow in the figure above shows netflow export from the additional network card on the server.
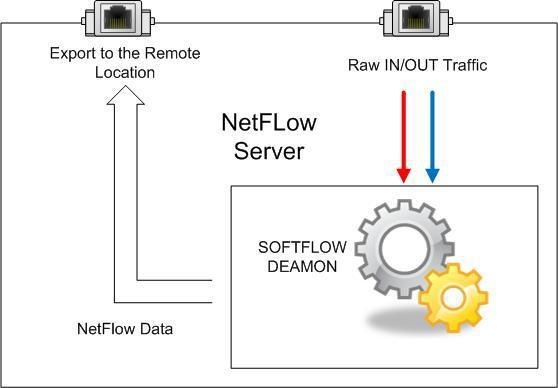
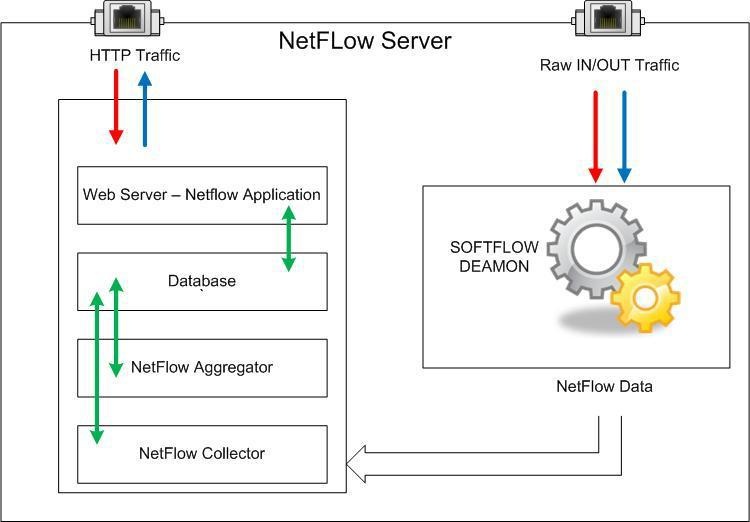
Now, it is possible to start the netflow probe on the NetFlow Daemon Server. One of these applications is the SoftFlowd that has the possibility of exporting netflow traffic locally (127.0.0.1) to the UDP port on the same server or to a UDP port on a remote server.
Above figures show examples of local netflow export and remote netflow export.