Versions Compared
Key
- This line was added.
- This line was removed.
- Formatting was changed.
The following explains in which situations is better to use incoming (in/Ingress ) or outgoing (out/Egress) flow on the interface for collecting NetFlow statistics.
Incorrect NetFlow Export
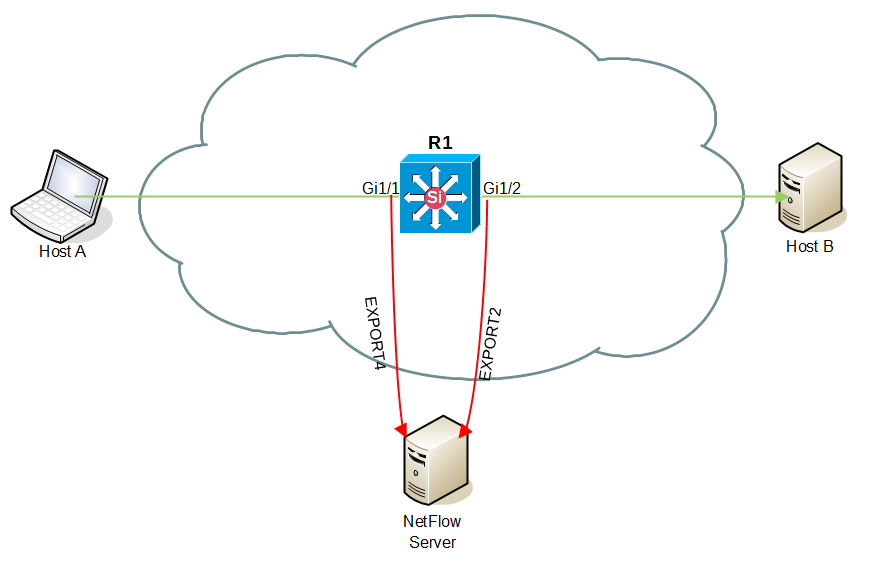 Image Removed
Image Removed
On the above figure you can see that interfaces Gi1/1 and Gi1/2 are set to collect NetFlow statistics, Gi1/1 in IN direction and Gi1/2 in OUT direction. This example shows that a flow traveling from Host A to Host B will be collected and exported twice to NetFlow server, while a flow traveling from Host B to Host A will not be matched and exported. The result is a false NetFlow statistic: double amount of flows for A to B direction, and zero flows for B to A direction.
| Note |
|---|
| It is very important that all interfaces on a single device are configured to collect flow in only one direction, IN or OUT. |
Correct NetFlow Export
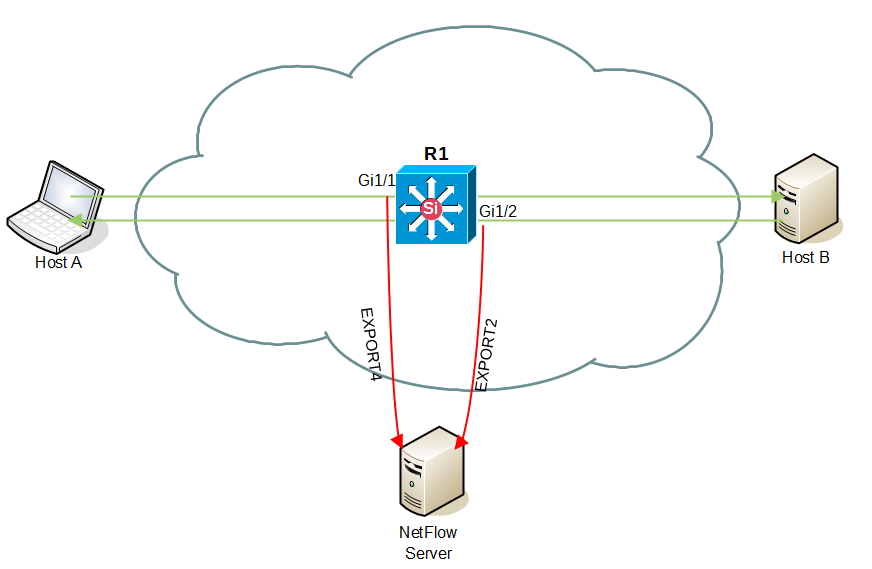 Image Removed
Image Removed
Here, both interface Gi1/1 and interface Gi1/2 are set to collect the NetFlow statistics in IN direction. This time, a flow traveling from Host A to Host B will be collected only once, and a flow traveling from Host B to Host A will be collected as well. Now, NetFlow statistics will be correct and none of the charts in TopN > Exporters will have duplicated data.
Ingress or Egress?
| Info |
|---|
| When considering to configure Ingress or Egress flow on an exporter device, you must be aware that it depends on software version and supervisor module (if existing). For this information, please check release notes of your device vendor. |
Ingress export enabled on all the interfaces of a device switch or router will in general deliver all necessary information.NetFlow v9 supports Ingress and Egress, but NetFlow v5 only supports Ingress flows. If your device is only supported by NetFlow needed information, in most situations. If device only supports NetFlow v5, your flows should necessarily be Ingress. necessarily be configured in Ingress direction, because NetFlow v5 only supports Ingress flows. In addition, Ingress export provides monitoring of Blocked traffic (traffic sent to Interface Out 0).Egress should be considered in these situations
Here are a few exceptions where using Egress Flows is suitable:
- Some routers devices (e.g. Cisco WAAS, Riverbed, etc.) have an option to compress flows, so the Out traffic will be significantly more than In traffic. Egress export provides more precise information on traffic transferred in the networkyou need to see traffic after it was compressed. Egress flows are calculated after compression.
- When multicast flows are sent, Ingress exported flows have a destination interface 0 because the router doesn’t know interface Out before processing. Egress exported flows deliver the destination interfaces , and in addition if and if the flow is headed for multiple interfaces it will be exported as multiple flows.
- When exporting NetFlow on only one interface of the router or switch.
| Warning |
|---|
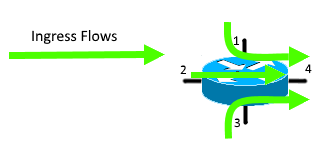
When using only ingress flows, it is important to enable NetFlow data export on all interfaces, because outbound utilization on any given interface is calculated by using ingress flows from other interfaces. See example at the figure below. If you have not enabled NetFlow on interface 2, flows going through that interface will be missed when calculating outbound utilization on interface 4.
|
| Warning |
|---|
You should configure interfaces on a single device to collect flows in only one direction (either Ingress or Egress), so that flows traveling from one host to another and vice versa are collected only once.  Image Added Image Added |
Continue reading on to Choosing Exporters.
| Tip |
|---|
In Flexible NetFlow, Input and Output do the same as Ingress and Egress in Traditional NetFlow. |